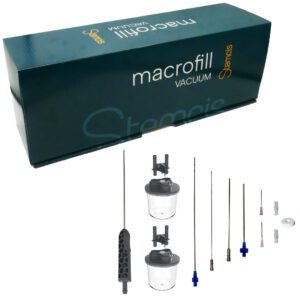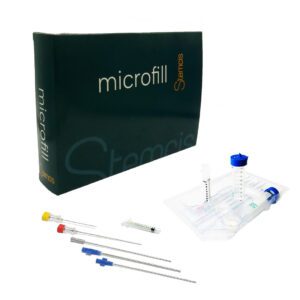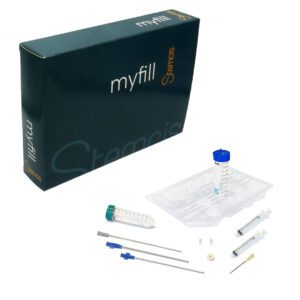

Most popular kits
Designed to bring you maximum comfort
Our kits have been thoughtfully designed by surgeons for surgeons to bring them optimum comfort in their practice: easy and pleasant to use with an ideal grip, sterile and single-use for greater safety, and at the cutting edge of technology to place you ahead of the field.
- Treat yourself to more convenience and peace of mind
- Save time during surgery
- Preserve all the benefits of the adipose tissue
- Guarantee your patients the best results
- Focus solely on the work at hand
- Use Stemcis kits.






Designed for countless procedures
Whatever your specialty – cosmetic/reconstructive surgery, orthopaedic surgery, gynaecological surgery or even dermatology, our kits adapt to your practice. From small (1 – 10 mL) to large (150 – 200 mL) volumes, with or without implants, you will always find a STEMCIS kit that suits your needs.